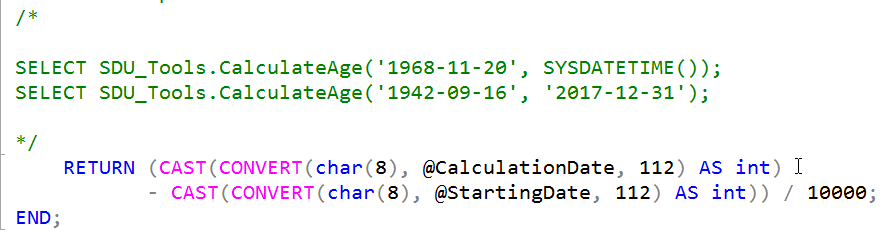
SSMS Tips and Tricks 2-7: Making sense of the colors in the SSMS scroll bar
In an earlier post, I described how I didn’t particularly like all the colors that are shown in the scroll bar now in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
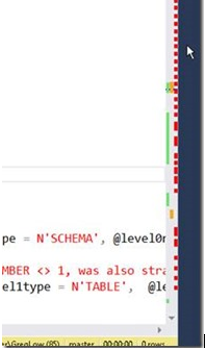
In that post, I described how to turn them all off, or at least how to kill off some of them. But, of course they are there for a reason.
Instead of turning them all off, you might decide to make sense of what they are there for. The colors that are displayed indicate the following:
2025-06-14