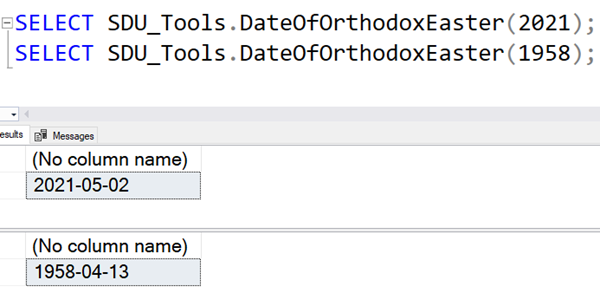
SDU Tools: Date of Orthodox Easter in SQL Server T-SQL
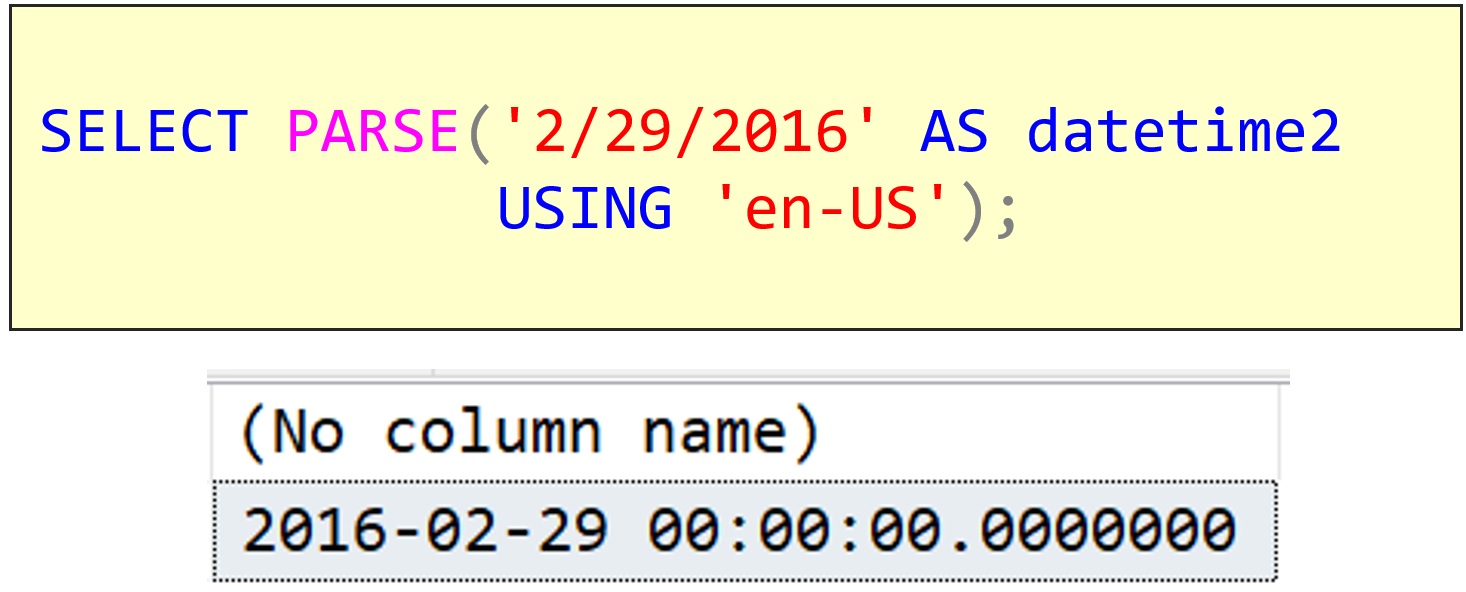
Some time back, we added DateOfEasterSunday to our free SDU Tools for developers and DBAs. Given it was the Christian Easter Sunday, almost immediately, I got a request for the Greek Orthodox Easter. That date isn’t of course just the Greek one, so we’ve added a new function DateOfOrthodoxEaster.
It’s based on a concept from Antonios Chatzipavlis. Thanks !
It takes a single parameter:
@Year int - the year to find the date for
2021-02-12