SQL: Computed Columns: It's a matter of persistence
Most SQL Server developers are aware that they can create computed columns. We do that by defining a column AS some expression like this:
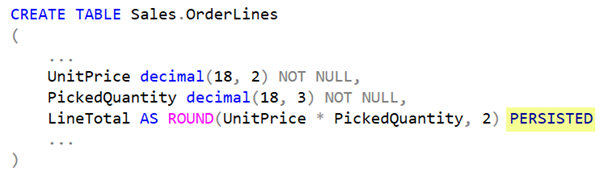
CREATE TABLE Sales.OrderLines
(
...
UnitPrice decimal(18, 2) NOT NULL,
PickedQuantity decimal(18, 3) NOT NULL,
LineTotal AS ROUND(UnitPrice * PickedQuantity, 2)
...
)
Each time the value from that LineTotal column is queried, the calculation is performed so the result can be returned. This makes sense when the value is changing regularly and the value is queried infrequently.
2026-03-07