SQL: sys.dm_fts_parser for Full-Text Word Breaking
One of my favorite DMFs that most people seem to be completely unaware of, is sys.dm_fts_parser(). It allows you to see the result of the word-breaking occurring within full text search. If you execute the query:
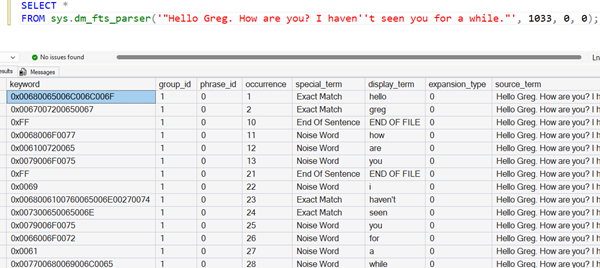
SELECT *
FROM sys.dm_fts_parser('"Hello Greg. How are you? I haven''t seen you for a while."', 1033, 0, 0);
It returns the following data (along with some other columns):
| occurrence | special_term | display_term |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Exact Match | hello |
| 2 | Exact Match | greg |
| 10 | End Of Sentence | END OF FILE |
| 11 | Noise Word | how |
| 12 | Noise Word | are |
| 13 | Noise Word | you |
| 21 | End Of Sentence | END OF FILE |
| 22 | Noise Word | i |
| 23 | Exact Match | haven’t |
| 24 | Exact Match | seen |
| 25 | Noise Word | you |
| 26 | Noise Word | for |
| 27 | Noise Word | a |
| 28 | Noise Word | while |
| 36 | End Of Sentence | END OF FILE |
That’s really impressive as it lets you parse text into words. The 1033 was the locale I chose (for US English) and the other two parameters were a stop word list (formerly called a noise word list) and whether or not it should be accent sensitive.
2026-02-03






